Have you heard of shock loss before? Are you afraid it might happen to you? So what should you know about the causes, solutions, and process of shock loss?
Hair transplantation is one of the effective and permanent methods that many people experiencing hair loss problems resort to today. However, after the transplantation process, some patients may experience a condition called “shock loss,” which causes concern for those who are unaware of this type of hair loss. Although this condition can be worrying for those experiencing it for the first time, it is actually a natural part of hair transplantation. In this article, we will address the causes of shock loss after hair transplantation, the process, how long it lasts, and what should be done during this period in detail to alleviate your concerns.
İçindekiler
What is Shock Loss?
Approximately 2 to 6 weeks after the hair transplant operation, most of the transplanted hair will begin to fall out. This shedding is called “shock loss.” In fact, this shedding does not mean that the hair follicles have been damaged or that the hair transplant has failed. On the contrary, it is a temporary and important stage in preparation for the new hair growth process. The transplanted follicles remain firmly in place under the skin; only the upper strands fall out.
The most noticeable feature of shock loss is that it occurs rapidly and in large numbers. Therefore, patients may think that their hair has been wasted. However, after this stage, the hair follicles enter a dormant phase, and within a few months, new, permanent hair begins to grow.
Why Does It Occur?
Shock loss is a normal process seen in 80-90% of people who undergo hair transplantation. The underlying causes of this loss are as follows:
• Trauma Effect: During hair transplantation, hair follicles are transplanted to a new area. This creates a short-term shock for the follicles.
• Change in Blood Circulation: Blood flow to the area where the new grafts are located increases over time. During this adaptation process, the old hairs fall out.
• Natural Hair Cycle: Hair goes through anagen (growth), catagen (transition), and telogen (shedding) phases. Shock loss is an accelerated version of this cycle.
• Stress and Recovery Process: The post-operative recovery period requires an adaptation process in the hair follicles, as it does throughout the body.
How Long Does Shock Loss Last?
Shock loss usually begins in the second week after transplantation and can continue for up to 6-8 weeks. However, this may vary from person to person. Most patients see most of their hair lost by the end of the second month.
However, there is no cause for concern, as this is completely temporary. Starting in the third month, new hair strands begin to emerge from the transplanted follicles. By the end of the first year, 90% of the hair will be visibly visible. Hair growth occurs in four stages. Each stage plays an important role in the hair’s life cycle. The four stages are as follows:
- Anagen (growth phase)
- Catagen Phase (Transition Phase)
- Telogen Phase (Resting Phase)
- Exogen (shedding phase)
Final results are typically achieved within 12-18 months.
What Should Be Done During This Period?
The shock loss process is a period that requires patience. Here are some points to keep in mind to get through this process with peace of mind:
1. Follow Your Doctor’s Advice: You must strictly follow your doctor’s instructions regarding hair washing methods, lotions, and medications. 2. Don’t Panic: Shock hair loss is a natural process. There is no need to worry or seek alternative treatments. 3. Pay Attention to Your Diet: Foods rich in protein, zinc, biotin, and B vitamins help strengthen hair roots. 4. Avoid Smoking and Alcohol: These habits negatively affect blood circulation and can slow down the hair growth process. 5. Stay Away from Stress: Psychological stress can negatively affect the body’s healing process. Adopting a calmer lifestyle during this period is beneficial.
The Difference Between Shock Loss and Permanent Hair Loss
Many patients may confuse shock loss with permanent hair loss. The differences can be summarized as follows:
- In shock loss, only the hair strands are lost; the roots remain alive.
- In permanent hair loss, the roots are damaged and hair does not grow back.
- Shock loss typically occurs within the first few months, while permanent loss progresses over time, often due to genetic factors.
Therefore, even if intense shedding occurs after hair transplantation, the hair will grow back because the roots are healthy.
Is it possible to reduce shock loss?
Shock loss cannot be completely prevented because it is one of the natural outcomes of hair transplantation. However, some methods can be used to reduce its effects:
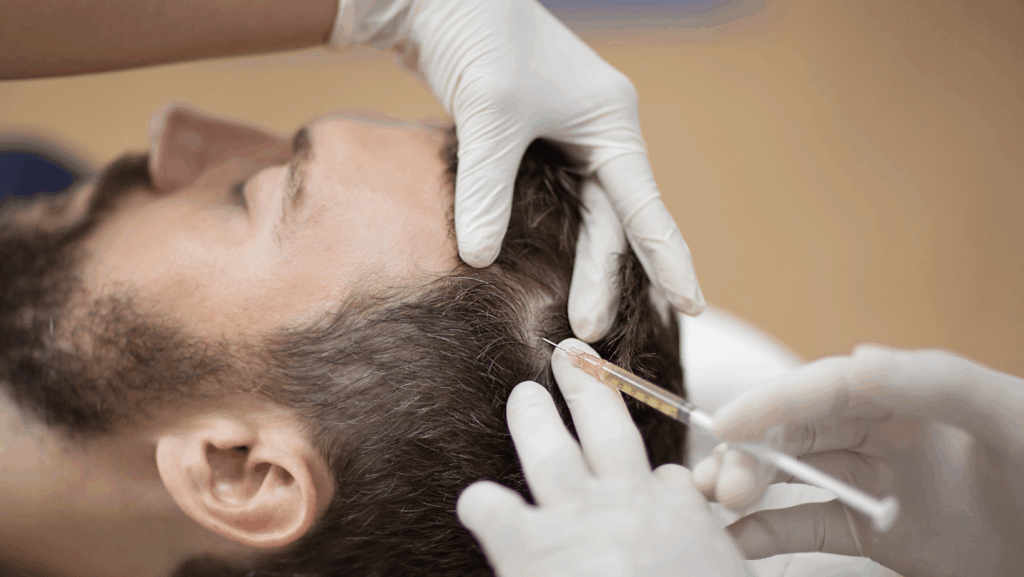
• PRP (Platelet Rich Plasma) Treatment: Plasma obtained from the person’s own blood is injected into the transplanted area to help the roots recover more quickly. • Mesotherapy: Vitamin and mineral injections support the nourishment of hair follicles. • Regular Check-ups: Visiting the doctor at specific intervals after the transplant ensures a healthier progression of the process.
Conclusion
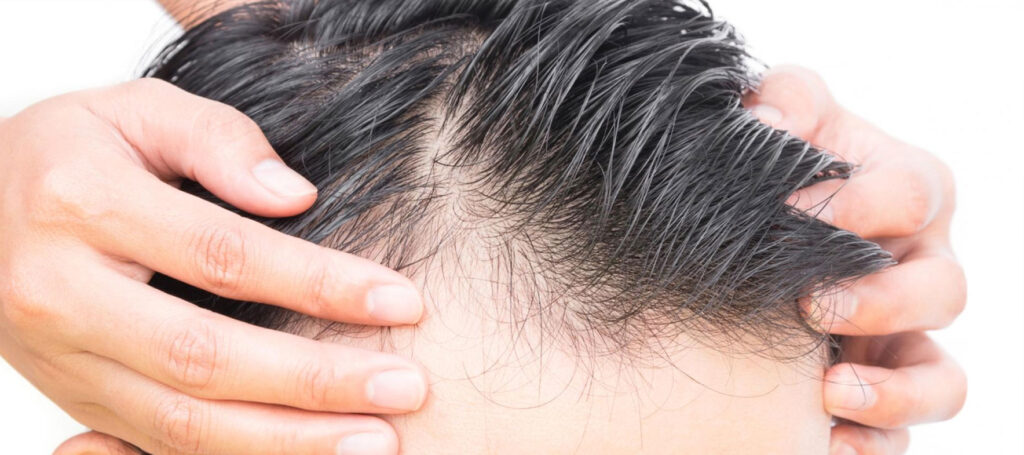

Shock loss after hair transplantation is one of the most natural and expected stages of the process. Since the roots remain intact, the lost hairs are replaced by stronger, permanent, and natural hair. During this period, it is crucial to be patient, follow the doctor’s recommendations, and maintain healthy lifestyle habits.
In short, shock loss does not mean that the hair transplant has failed; on the contrary, it is a sign that new hair will grow back stronger.
Hairtrans.com was founded by world-famous plastic surgeon Dr. MFO, who is an expert in facial feminization or facial masculinization surgeries, and is managed under his leadership. Would you like to have a hair transplant under the coordination of a plastic surgeon with many years of experience?
Whether you are a trans woman or a natural born male or female, if you are looking for the best hair transplant, contact us now.